Who invented electricity?
Firstly electricity wan’t necessarily invented as it is a naturally occuring form of energy. By the same token there wasn’t just one pioneer of electricity either, since there were a handful of genius’ attempting to solve the complex puzzle at the same time.
Unorthodoxly electricity was first discovered by the Greeks whom unintentionally observed that by rubbing fossilised tree resin with animal fur it unexpectedly made the resin attract the dried grass, this was indeed static electricity. A fascinating discovery during an archaeological dig in the 1930’s uncovered pots constructed with an inside copper lining. More interesting archeologists understand them to be ancient batteries designed to supply lighting at Roman sites.
[caption id="attachment_937" align="alignnone" width="300"]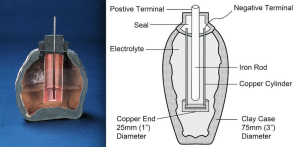 Ancient electric batteries[/caption]
During the 17th century there were numerous electricity related discoveries including Benjamin Franklins famous kite experiment during a storm, however that only demonstrated that lighting was identical to a short electric spark. The first dynamic electricity (the flow of an electrical charge through a conduction point or more readily known as an electric current) discovery would hands down lie with an Italian physicist named Alessandro Volta. Volta soon realised that a chemical reaction could create electricity moreover in 1800 he assembled possibly the first electric battery to provide a stable electric current. You may of also picked up on Alessandro distinguishable surname Volta which became the official measuring units of electric potential (known as volts) in tribute to his discoveries.
[caption id="attachment_938" align="alignnone" width="300"]
Ancient electric batteries[/caption]
During the 17th century there were numerous electricity related discoveries including Benjamin Franklins famous kite experiment during a storm, however that only demonstrated that lighting was identical to a short electric spark. The first dynamic electricity (the flow of an electrical charge through a conduction point or more readily known as an electric current) discovery would hands down lie with an Italian physicist named Alessandro Volta. Volta soon realised that a chemical reaction could create electricity moreover in 1800 he assembled possibly the first electric battery to provide a stable electric current. You may of also picked up on Alessandro distinguishable surname Volta which became the official measuring units of electric potential (known as volts) in tribute to his discoveries.
[caption id="attachment_938" align="alignnone" width="300"] Alessandro Volta - electric pioneer[/caption]
Electricity really only became accessible for technology pioneers in 1831 when Michael Faraday paved the way for the prominent innovator Thomas Edison and a lesser recognised British scientist Joseph Swan whom each invited the incandescent filament light bulb. Faraday effectively designed the first electric dynamo which found the answer to generating an electric current in a continuous and feasible manner. Edison and Swan soon after teamed up to manufacture the first filament lamp of which Edison integrated his direct current system (DC) which supplied electricity to illuminate New Yorks first electric street lamps.
There were many more significant players whom developed the application of electricity, whom went on to signifying production on a viable scale to where it is today. Some of the developers include Scottish James Watt whom recognisably had the derived unit of power named after him, Andre Ampere and George Ohm. Having said that electricity hasn’t stopped evolving and is still developing today furthermore with it’s potential to be powered by carbon free renewable sources it is seen as our number one power source of the future. So much technology has sprung out of electricity much of which you may take for granted. Just take a look around your home, televisions, tablets, iPhones, microwaves, electric radiators, lights and even your car which all feature electricity. It really makes you wonder where we would be without it since it makes our lives so much easier.
[caption id="attachment_939" align="alignnone" width="300"]
Alessandro Volta - electric pioneer[/caption]
Electricity really only became accessible for technology pioneers in 1831 when Michael Faraday paved the way for the prominent innovator Thomas Edison and a lesser recognised British scientist Joseph Swan whom each invited the incandescent filament light bulb. Faraday effectively designed the first electric dynamo which found the answer to generating an electric current in a continuous and feasible manner. Edison and Swan soon after teamed up to manufacture the first filament lamp of which Edison integrated his direct current system (DC) which supplied electricity to illuminate New Yorks first electric street lamps.
There were many more significant players whom developed the application of electricity, whom went on to signifying production on a viable scale to where it is today. Some of the developers include Scottish James Watt whom recognisably had the derived unit of power named after him, Andre Ampere and George Ohm. Having said that electricity hasn’t stopped evolving and is still developing today furthermore with it’s potential to be powered by carbon free renewable sources it is seen as our number one power source of the future. So much technology has sprung out of electricity much of which you may take for granted. Just take a look around your home, televisions, tablets, iPhones, microwaves, electric radiators, lights and even your car which all feature electricity. It really makes you wonder where we would be without it since it makes our lives so much easier.
[caption id="attachment_939" align="alignnone" width="300"] electricity dial[/caption]
In 1839 Alexandre Becquerel recognised the photovoltaic reaction which illustrated how electricity could be produced through direct sunlight. Although nothing really became of this breakthrough until 1941 when Russell Ohl created the silicon solar cell however it wasn’t until 1954 when American researcher Gerald Pearson and his team we able to produce a solar panel which had an efficiency level of just 6% accompanied by direct sunlight. Fast forward to today and it’s forecast that by 2020 10 million UK households could be fitted with solar panels. Technology is making a dramatic shift into a new age of low carbon electricity, which is perfect for running the latest eco electric radiators. In 2016 plans to construct the UK’s largest power plant named Hinkley point C were stalled for numerous reasons. The controversial project was designed to offer significant support to the UK’s electricity supply, nevertheless there has recently been a switch in government him are reassessing the proposal and have recognised that the nuclear technology involved controversially remains untested. On top of this there are much more efficient and established electricity generating technologies out there which offer a more competitive price per Megawatt which is why the latest government is re-evaluating the scheme. Even hundreds if not thousands of years on from the first discovery of electricity the application of scientific knowledge surrounding the energy is yet to reach it’s pinnacle and it’s sure to say it doesn’t look like stopping any time soon.
5 fascinating facts your may not be aware about electricity
electricity dial[/caption]
In 1839 Alexandre Becquerel recognised the photovoltaic reaction which illustrated how electricity could be produced through direct sunlight. Although nothing really became of this breakthrough until 1941 when Russell Ohl created the silicon solar cell however it wasn’t until 1954 when American researcher Gerald Pearson and his team we able to produce a solar panel which had an efficiency level of just 6% accompanied by direct sunlight. Fast forward to today and it’s forecast that by 2020 10 million UK households could be fitted with solar panels. Technology is making a dramatic shift into a new age of low carbon electricity, which is perfect for running the latest eco electric radiators. In 2016 plans to construct the UK’s largest power plant named Hinkley point C were stalled for numerous reasons. The controversial project was designed to offer significant support to the UK’s electricity supply, nevertheless there has recently been a switch in government him are reassessing the proposal and have recognised that the nuclear technology involved controversially remains untested. On top of this there are much more efficient and established electricity generating technologies out there which offer a more competitive price per Megawatt which is why the latest government is re-evaluating the scheme. Even hundreds if not thousands of years on from the first discovery of electricity the application of scientific knowledge surrounding the energy is yet to reach it’s pinnacle and it’s sure to say it doesn’t look like stopping any time soon.
5 fascinating facts your may not be aware about electricity
 Ancient electric batteries[/caption]
During the 17th century there were numerous electricity related discoveries including Benjamin Franklins famous kite experiment during a storm, however that only demonstrated that lighting was identical to a short electric spark. The first dynamic electricity (the flow of an electrical charge through a conduction point or more readily known as an electric current) discovery would hands down lie with an Italian physicist named Alessandro Volta. Volta soon realised that a chemical reaction could create electricity moreover in 1800 he assembled possibly the first electric battery to provide a stable electric current. You may of also picked up on Alessandro distinguishable surname Volta which became the official measuring units of electric potential (known as volts) in tribute to his discoveries.
[caption id="attachment_938" align="alignnone" width="300"]
Ancient electric batteries[/caption]
During the 17th century there were numerous electricity related discoveries including Benjamin Franklins famous kite experiment during a storm, however that only demonstrated that lighting was identical to a short electric spark. The first dynamic electricity (the flow of an electrical charge through a conduction point or more readily known as an electric current) discovery would hands down lie with an Italian physicist named Alessandro Volta. Volta soon realised that a chemical reaction could create electricity moreover in 1800 he assembled possibly the first electric battery to provide a stable electric current. You may of also picked up on Alessandro distinguishable surname Volta which became the official measuring units of electric potential (known as volts) in tribute to his discoveries.
[caption id="attachment_938" align="alignnone" width="300"] Alessandro Volta - electric pioneer[/caption]
Electricity really only became accessible for technology pioneers in 1831 when Michael Faraday paved the way for the prominent innovator Thomas Edison and a lesser recognised British scientist Joseph Swan whom each invited the incandescent filament light bulb. Faraday effectively designed the first electric dynamo which found the answer to generating an electric current in a continuous and feasible manner. Edison and Swan soon after teamed up to manufacture the first filament lamp of which Edison integrated his direct current system (DC) which supplied electricity to illuminate New Yorks first electric street lamps.
There were many more significant players whom developed the application of electricity, whom went on to signifying production on a viable scale to where it is today. Some of the developers include Scottish James Watt whom recognisably had the derived unit of power named after him, Andre Ampere and George Ohm. Having said that electricity hasn’t stopped evolving and is still developing today furthermore with it’s potential to be powered by carbon free renewable sources it is seen as our number one power source of the future. So much technology has sprung out of electricity much of which you may take for granted. Just take a look around your home, televisions, tablets, iPhones, microwaves, electric radiators, lights and even your car which all feature electricity. It really makes you wonder where we would be without it since it makes our lives so much easier.
[caption id="attachment_939" align="alignnone" width="300"]
Alessandro Volta - electric pioneer[/caption]
Electricity really only became accessible for technology pioneers in 1831 when Michael Faraday paved the way for the prominent innovator Thomas Edison and a lesser recognised British scientist Joseph Swan whom each invited the incandescent filament light bulb. Faraday effectively designed the first electric dynamo which found the answer to generating an electric current in a continuous and feasible manner. Edison and Swan soon after teamed up to manufacture the first filament lamp of which Edison integrated his direct current system (DC) which supplied electricity to illuminate New Yorks first electric street lamps.
There were many more significant players whom developed the application of electricity, whom went on to signifying production on a viable scale to where it is today. Some of the developers include Scottish James Watt whom recognisably had the derived unit of power named after him, Andre Ampere and George Ohm. Having said that electricity hasn’t stopped evolving and is still developing today furthermore with it’s potential to be powered by carbon free renewable sources it is seen as our number one power source of the future. So much technology has sprung out of electricity much of which you may take for granted. Just take a look around your home, televisions, tablets, iPhones, microwaves, electric radiators, lights and even your car which all feature electricity. It really makes you wonder where we would be without it since it makes our lives so much easier.
[caption id="attachment_939" align="alignnone" width="300"] electricity dial[/caption]
In 1839 Alexandre Becquerel recognised the photovoltaic reaction which illustrated how electricity could be produced through direct sunlight. Although nothing really became of this breakthrough until 1941 when Russell Ohl created the silicon solar cell however it wasn’t until 1954 when American researcher Gerald Pearson and his team we able to produce a solar panel which had an efficiency level of just 6% accompanied by direct sunlight. Fast forward to today and it’s forecast that by 2020 10 million UK households could be fitted with solar panels. Technology is making a dramatic shift into a new age of low carbon electricity, which is perfect for running the latest eco electric radiators. In 2016 plans to construct the UK’s largest power plant named Hinkley point C were stalled for numerous reasons. The controversial project was designed to offer significant support to the UK’s electricity supply, nevertheless there has recently been a switch in government him are reassessing the proposal and have recognised that the nuclear technology involved controversially remains untested. On top of this there are much more efficient and established electricity generating technologies out there which offer a more competitive price per Megawatt which is why the latest government is re-evaluating the scheme. Even hundreds if not thousands of years on from the first discovery of electricity the application of scientific knowledge surrounding the energy is yet to reach it’s pinnacle and it’s sure to say it doesn’t look like stopping any time soon.
5 fascinating facts your may not be aware about electricity
electricity dial[/caption]
In 1839 Alexandre Becquerel recognised the photovoltaic reaction which illustrated how electricity could be produced through direct sunlight. Although nothing really became of this breakthrough until 1941 when Russell Ohl created the silicon solar cell however it wasn’t until 1954 when American researcher Gerald Pearson and his team we able to produce a solar panel which had an efficiency level of just 6% accompanied by direct sunlight. Fast forward to today and it’s forecast that by 2020 10 million UK households could be fitted with solar panels. Technology is making a dramatic shift into a new age of low carbon electricity, which is perfect for running the latest eco electric radiators. In 2016 plans to construct the UK’s largest power plant named Hinkley point C were stalled for numerous reasons. The controversial project was designed to offer significant support to the UK’s electricity supply, nevertheless there has recently been a switch in government him are reassessing the proposal and have recognised that the nuclear technology involved controversially remains untested. On top of this there are much more efficient and established electricity generating technologies out there which offer a more competitive price per Megawatt which is why the latest government is re-evaluating the scheme. Even hundreds if not thousands of years on from the first discovery of electricity the application of scientific knowledge surrounding the energy is yet to reach it’s pinnacle and it’s sure to say it doesn’t look like stopping any time soon.
5 fascinating facts your may not be aware about electricity
- Electricity moves at the speed of light, which is more than 186,000 miles a second!
- Electricity is involved in your heartbeat allowing it to contract. You may be familiar with an ECG machine especially if you’ve ever seen a hospital scene on TV. The ECG machine displays a line gently moving across a monitor with frequent spikes.
- Benjamin Franklin invented the lightning rod which is typically fitted to summit of a property which conducts a lightning strike through a grounded wire keeping the building safe.
- Eels produce a strong electric shock of 500 volts which they use for defending themselves and catching pray
- Renewable electricity is forecast to overtake fossil fuel generated electricity due to it being cheaper and low carbon.


